I thought I would copy and paste this from Doc Griffin from this thread on fish feeds.
http://www.pondboss.com/forums/ubbthreads.php?ubb=showflat&Number=117414&fpart=1Typical BG food
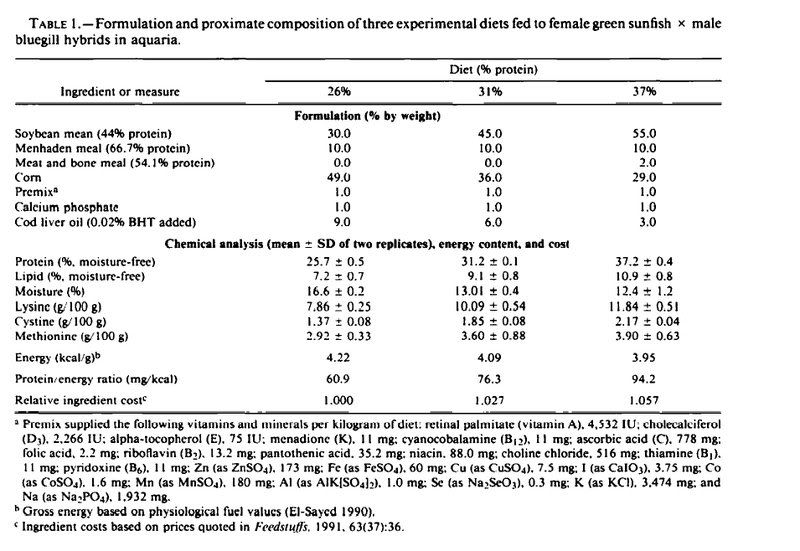
Catfish feed
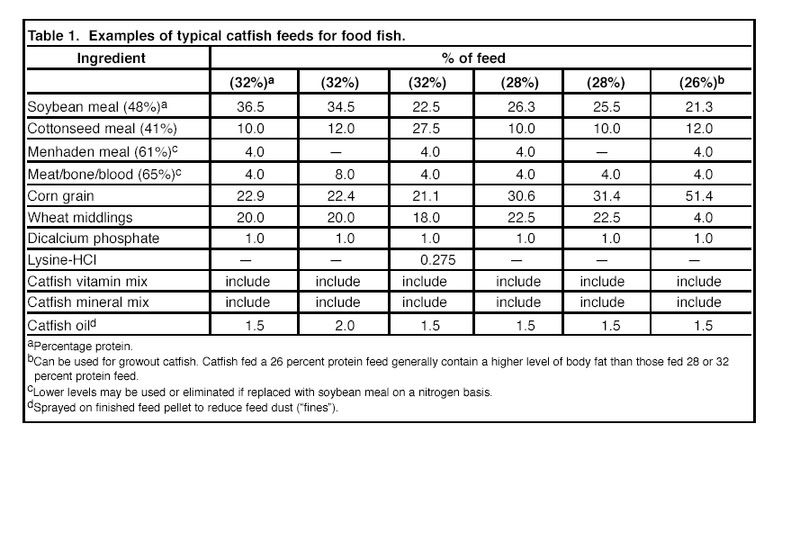
MEG
Feather meal as a fish food protein source. There are two primary factors of protein quality for monogastrics (fish for this discussion) - 1) Amino Acid profile and 2) Amino Acid availability. The amino acid profile of feather looks pretty good if you look at the Total Sulfur Amino Acid content. It has a high content of cystine - a sulfur amino acid (SAA). SAAs can be limiting in monogastric diets and tend to be expensive to formulate into diets (they are relatively low in many inexpensive plant proteins). Unfortunately, the reason it is so high is because feather is a structural protein. The di-sulfide bonds between two cysteines make the protein very tough. This is what gives the keratins their structural rigidity - like our hair and fingernails. Unfortunately, this serves to make them very hard to digest. Therefore, as a rule, the availability is not so good. To increase the availability, feather meal is often hydrolyzed, this is an attempot to break down the disulfide bonds to increase availability. Shoe leather analyzes at 85% crude protein, but it is not digestible.
A word on protein sources.... Most protein sources are available in different qualities. This is particularly true for the expensive animal proteins - fish meal, poultry meals, blood meals, etc. Quality and freshness of the raw materials and the processing are factors that result in this variability. As examples:
A) Quality of Raw Materials: Meat meals are often priced on protein content - simply put, it is the ratio of bone (ash) to meat (protein). Bones (minerals, ash) are not as valuable as protein.
B) Freshness of Raw Materials: The US commercial fishing fleet for menhaden now has all refrigerated vessel storage.... the season is in over the summer, primarily in the Gulf of Mexico. Obviously, if it is not refrigerated....
c) Processing: Blood has a good amino acid profile. If it is drum-dried (essentially scorched on a extremely hot steel drum) it has poor availability and is a fairly poor ingredient. If it has been spray dried under low heat - it is an excellent ingredient.
High quality fish meal is the gold standard - it has the best Amino acid profile for fish (fish protein to grow fish protein)and is highly digestible. Further, it tastes great to fish (fish meal based diets are much more palatable to carnivorous fish) and it contains about 10% fish oil (high in omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids). Many other proteins can be used as long as they are formulated properly into an overall dietary amino acid profile.
Holler if you have questions. MEG
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ewest
Doc G can you give us some guidance on lipids (in pellets and or forage fish) as a necessary part of what carnivorous warm water fish (BG, LMB and HSB) need for winter survival ? Do most of them come from the fish meal (or fish oil in live forage) or elsewhere ?
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MEG
Well, today I see that Yahoo has a story on the importance of omega 3 fatty acids for us humans. For most of us, the source is fish - salmon, tuna, sardines, etc. I have not seen the data - but, for winter survival, the idea is that fish oil is a fluid. This enhance membrane fluidity. This is often cited as a reason for the role of PUFAs with brain function/development. When the water gets cold, the fish get cold. Therefore, it stands to reason that these fats benefit the animals in cold conditions. If the overall fatty acid profile has too much saturated fat, their fat reserves will solidify in cold water - like tallow in cold water. These PUFAs are important in many other aspects besides the physical properties....
Predatory fish get these fats from the smaller fish they consume. They do not synthesize the long chain PUFAs. The source is from algae and these fats are passed on to algae-eating zooplankton and fish and move up the food chain. Menhaden are excellent sources of the omega 3 PUFAs, because they are fatty fish and about 25% of their fatty acids are the long chain PUFAs. So, in a prepared diet, you need either a significant amount of certain marine algaes, or fish oil or meal (approximately 10% of fish meal is fish oil - as a side note... this is because fish meal is mechanically expressed, so it does not get all the fat out. In solvent-extracted meals - such as soybean meal - there is vurtually no fat left).